Though technology is advanced, paper-based conventional data management system is still popular. But to a certain extent, the documentation is digitalised in the central servers. Compared to paper-based documentation, digital files are easier to handle. Except for a server failure or spyware, the digitalised system is a boon.
However, the traditional paper-based and digital-oriented healthcare management systems pose certain challenges, especially in the healthcare sector. The most pressing issue is the security breach and miscommunication. The possibility of hacking and data fabrication is inevitable in conventional healthcare systems. Several such news were flashed from different parts of the world. For instance, The Economic Times reported, “India’s health data faces the rising risk of breaches, cyberattacks”, tracing the Cowin portal data leakage. Personal information such as Aadhar IDs, mobile numbers, names and other health details were hacked or leaked. How can this be fixed??.One mode is blockchain.
Blockchain as a Solution
The article “Blockchain Opportunities in Healthcare” explained the fragmented nature of traditional systems, which makes the access and sharing of information to different healthcare providers a difficult task. The news report briefs the limitations of the conventional system and the necessity of blockchain technology in healthcare.

In the traditional system, a central authority keeps the data. The hackers, spies or malicious nodes hack or audit the data from the centralised system and sometimes delete or fabricate them. It is possible because, in a centralised system, the data is saved only by the authority or organisation. Cowin portal is an example of a centralised system, wherein the government stores the data in its centralised database. Blockchain technology is a solution to such a centralised system.
Blockchains are not affected by a single point of failure. Even if the hacker successfully hacks the information stored in one block, the rest of the blocks eliminate the malicious one. So, in the healthcare sector, the data remains unchanged. Blockchains are thus an effective mechanism to tackle the malicious user. Let’s discuss blockchain technology in detail.
What do you mean by Blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology is always misinterpreted as cryptocurrency, especially Bitcoin. But blockchain is the technology behind cryptocurrencies. The applicational level possibility of blockchain technology is not limited to being a mere cryptocurrency. As referred in the news articles, this peer-to-peer decentralised networking system is efficient in the sectors such as healthcare sector.
In a blockchain network, the transactions are stored in blocks. The blocks are chained together to form a chain called the blockchain. The blocks timestamp the data with digital signatures. There is a public and private key to validate the data or transactions. The data is transferred and stored in multiple nodes (users), making blockchain networks tamperproof.
Through transparent and immutable distributed ledger technology, blockchains safeguard the data from security breaches. Now, Let us consider how blockchain networks are used in the health sector.
Functioning of Blockchains in Healthcare
Blockchains can be used in hospitals and other healthcare-oriented areas to ensure data safety. When patient records are saved using blockchain technology, they can be accessed by different users with a unified view. Patients can securely save and share the data with healthcare providers as permissioned access.
Blockchains preserve and exchange patient data through servers. The secure and transparent nature of blockchain identifies medical malpractice or errors. It improves the analytical capability of medical records and avoids data manipulation by improving healthcare efficiency. The analytical capability identifies poor-quality medicines in the market. Blockchain in each transaction phase validates the authenticity of the medical supply.
There are permissionless blockchains, wherein the information can be traced by the public who has internet connectivity. However, the sensitive and private information of a patient is stored as a permissioned blockchain. Let us see how the private data of a patient is circulated in the permissioned blockchain network:
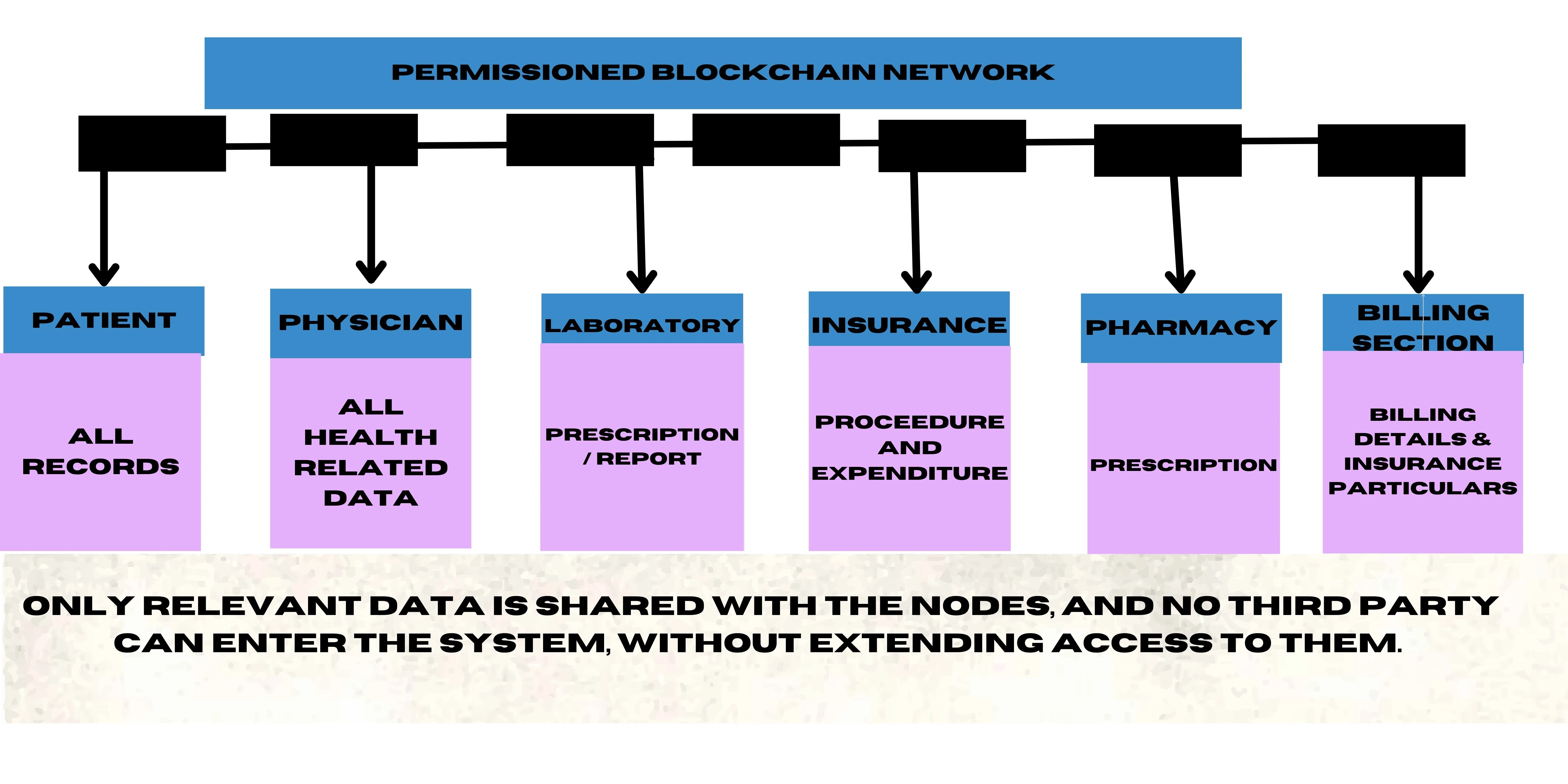
Here, the blockchain consists of six users: patient, physician, laboratory, insurance, pharmacy and billing. The data is protected, and the patient is the sole authority of the data. The patient can limit access, and the respective departments can only access the data related to the department. Even though the blocks are interconnected, the data access is denied in permissioned blockchain networks. Now, let’s see how blockchains are efficient in healthcare communication.
Blockchain in patient-medical practitioner interactions:
Patients benefit from blockchain’s smart contracts with automated insurance claims and an accurate billing process. When blockchain technology is used in the healthcare sector, it reduces the cost associated with the data management procedure. Blockchains are advised to protect privacy and for better interoperability in the health sector.
Doctors and patients can interact one-on-one using blockchain technology. Unlike other means of communication, blockchains are encoded with digital signatures. The digital signature generates trust and limits fraudulent interference. Blockchain guarantees the data anytime and anywhere. So, if the patient has to visit a different hospital or physician, the data will be available online.
Sometimes, the doctor might prescribe a specific drug, and the pharmacist provides a different drug. The drug provided by the pharmacist might not be a counterfeit, but the components in the medicine might vary. In such circumstances, the medicine might cause severe health issues rather than healing the disease. Is there any classification of blockchain based on the data type?
Blockchains based on the data type
Different types of blockchains can be used to customise the privacy of each individual. For public information distribution, public blockchain networks or permissionless blockchains are advised. However, personal or sensitive data can be added to a permissioned blockchain network as a private, hybrid, or consortium blockchain. Blockchain technology in healthcare is useful in different ways. The following image points out some of them.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Blockchain in the Health Sector
Blockchain networks have advantages and disadvantages like any other technology. Blockchain technology reduces the global distribution and consumption of counterfeit medicines. The network is immutable, and it resists data tampering and fraud.
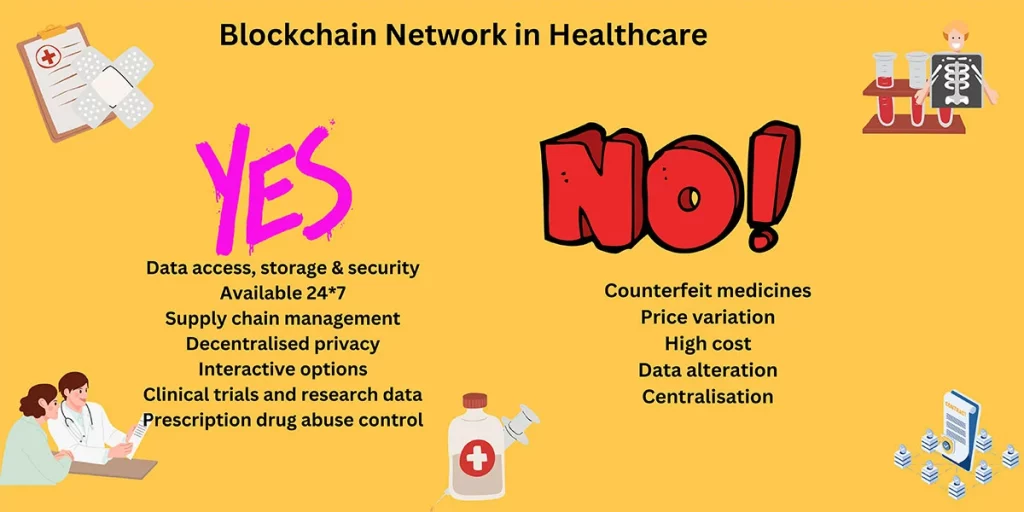
It reduces the chance of supplying counterfeit medicines and price variations. The smart contracts manage the data by maintaining the regulatory consensus set for the particular transaction. If you need clarification about smart contracts, continue reading the article.
Smart contracts improving data security
The smart contract consists of transparent clauses and conditions applicable to all nodes or users. When the block fulfils the criteria-based consensus, the contract is automatically executed. Such a feature reduces the need for intermediaries, and in the case of health insurance, smart contracts increase the speed. It is secure and efficient in transferring and storing medical reports. With limited access, permissioned blockchains are faster than permissionless blockchains.
Supply chain
Another issue lies in blockchain, which is in its supply phase, and the chances of counterfeit medicines entering the market are inevitable. However, with proper management of blockchain technology, it can be reduced to a great extent.
Centralisation in the decentralised system:
Private healthcare blockchains are centralised, with a limited number of participants. This type of blockchain is access-controlled, and it ensures the privacy and security of health-related data. But there is a chance of hacking when there are few participants. However, the blockchain is distributed and decentralised among limited participants.
Prescription drug abuse control:
Traditional paper-based prescriptions are manipulated. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recorded the estimated death of drug over-use in the United States as 108,000 in 2021. The death rate caused by drug overuse can be controlled with the traceable blockchain network. It keeps a record of the dispensed quantity of drugs.
To Conclude
From patient data management to insurance claims and bill settlements, blockchains are efficient in handling health-related data. Blockchain records and tracks the patient data or research and clinical outputs. So it is easier to access and transfer the data with identity authentication. Blockchain opportunities in healthcare are not limited, and several courses on blockchain technology create innumerable opportunities. The transparent ledger technology makes transactions and settlements easier, especially as tokens or cryptocurrencies.
Blockchains are secure, cost-effective, traceable, high speed, and confidential with token value, but there are some drawbacks as well. Generally, blockchains are unalterable and even for a genuine case, the timestamped blocks are not prone to edits. So, neither the patient nor medical professionals can change the entered data. Blockchains are still in the early phase of development, and the technology can be improved to remove such shortcomings.

