Blockchain technology is a cutting-edge database system that permits the transmission of information inside a network. It is a decentralised, distributed, and immutable ledger technology. Blockchain technology and Distributed ledgers are interconnected, and this article will highlight the interlinked connection between blockchains and distributed ledger technology. Learn foundation and advanced-level courses on blockchain technology!
Are Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology the same?
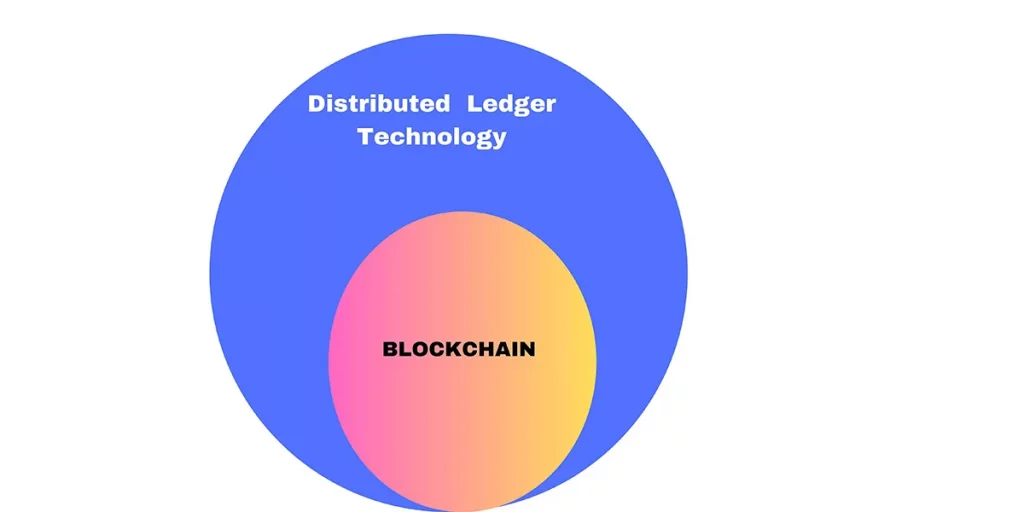
Distributed Ledger Technology is rooted in the distributed database. Blockchain is a type of distributed ledger technology. However, blockchain is the advanced version of distributed ledger technology. Permissionless and permissioned blockchains are the two access-based classifications of blockchain networks. It efficiently handles real-time issues on an application level.
As a distributed ledger technology, blockchain works without third-party supervision. The blockchains are capable of verifying peer-to-peer transactions through a decentralised ledger system. Blockchain technology and distributed ledger technology are synonymously used. But blockchain technology is not the operating technology of some DLT’s, and they are not the same. To understand the difference, let us discuss Distributed Ledger Technology first.
The basic Conceptualisation of Distributed Ledger Technology
Let us discuss DLT or Distributed Ledger Technology in detail. The core of Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is a distributed database that stores transaction-related data. Distributed ledgers are databases circulated among several nodes, computers, organisations, or nations. It is available to many users in the world. Distributed ledger technology uses smart contracts. They are immutable, fault-tolerant, distributed, transparent, secure, censorship-free, and decentralised.
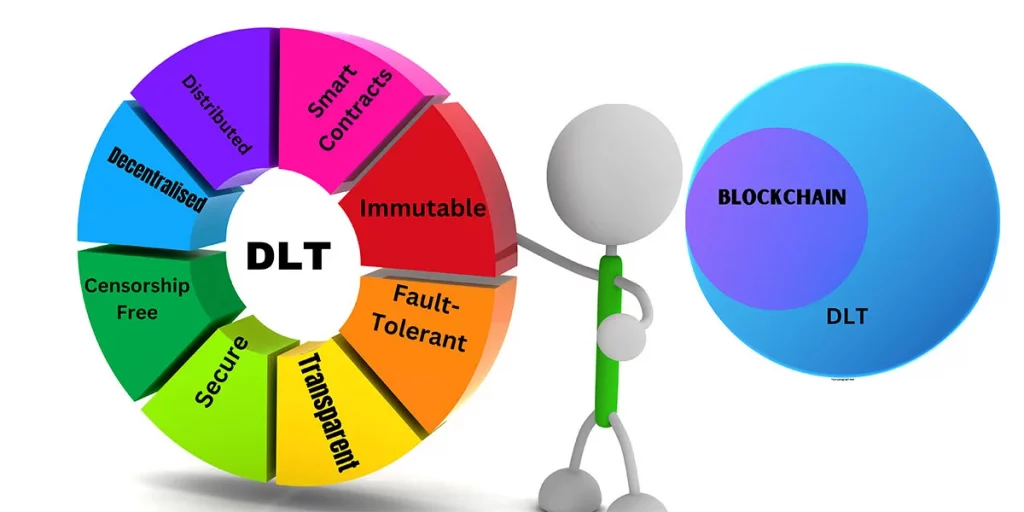
Blockchains use Distributed ledger technology, so the features of blockchains and distributed ledgers are similar. Blockchain uses distributed ledger technology, which is scalable. It records the transactions of assets and is shared with multiple nodes, creating copies. Thus, DLT’s decentralisation ensures data safety through its shared nature. Hackers or spies can fabricate or eliminate the data in a centralised system.
Possibility of data manipulation!
To manipulate the data, a hacker, spy, or malicious node has to identify the shared systems. After identifying all the nodes, the hacker should alter the data from all the nodes. It is time-consuming and requires a lot of energy. Depending on the public, private, permissioned, permissionless, and hybrid type, the number of users varies, with varying security levels.
In the DLT, blocks can be organised in different forms and use diferent consensus mechanisms. It does not use tokens or digital currency, and it does not require a sequence. It is trustworthy and faster, improves the auditing capability of transactions, and is unalterable.
Every node processes, verifies, and generates records of transactions, creating consensus in distributed ledger technology. To differentiate DLT from blockchain, it is necessary to understand blockchain. So, let us discuss about blockchains.
Explain what a blockchain is
Blocks are added as chains using a consensus protocol or algorithm. Tokens must be considered in this consensus, and blocks are sequentially arranged. Certain blockchains are mineable, and a miner takes the lead, which reduces trust among nodes. Blockchains are decentralised, which means they eliminate the conventional centralised system.
In a centralised system, all information is stored in a central server, which can be hacked easily. In a blockchain, the distributed ledger system keeps data at each node. It secures the information in a decentralised manner. Distributed ledgers use multiple nodes to record, share, and synchronise transactions. In blockchain networks, electronic ledgers use digital or cryptographic signatures. Blockchains are verifiable, time-stamped and tamperproof.
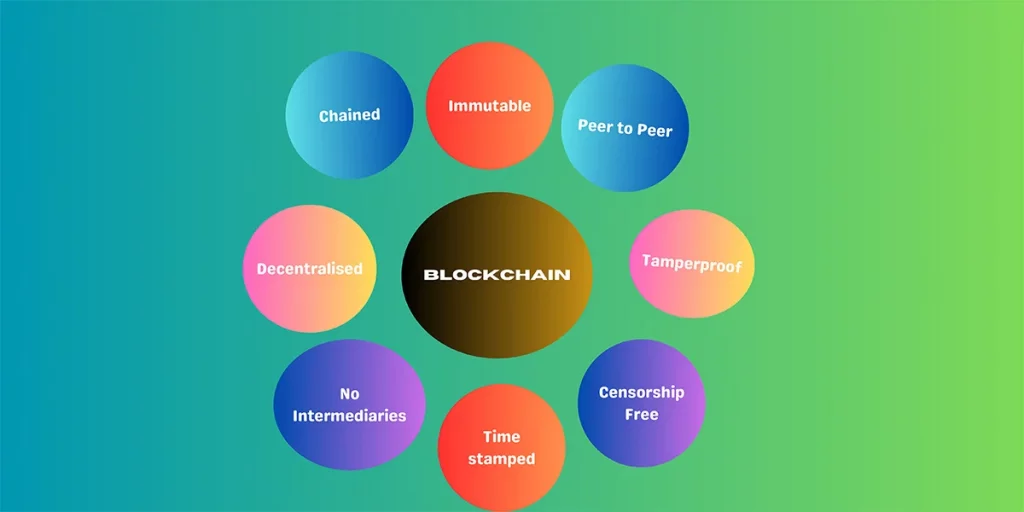
The best thing about blockchains is that they are not prone to censorship. It means that, unlike a centralised ledger system, nobody will filter, terminate, or censor the data stored in the blockchain. Blockchain technology uses proof-of-stake consensus, which reduces 99% of carbon emissions compared to Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus. So, Proof-of-Stake consensus-based blockchains are ecologically sustainable.
What are the components of a block?
Every block consists of a header and a body part. In the header part, the previous block’s hash value, timestamp, nonce, and Merle root are stored to resist cyber-attacks. The body part comprises the transaction details, including – the ‘addresses (from and to), data or value, and transaction hash’. A blockchain comprises blocks, nodes, nonce, hashes, and a ledger. There are four types of blockchains: public, private, consortium and hybrid.
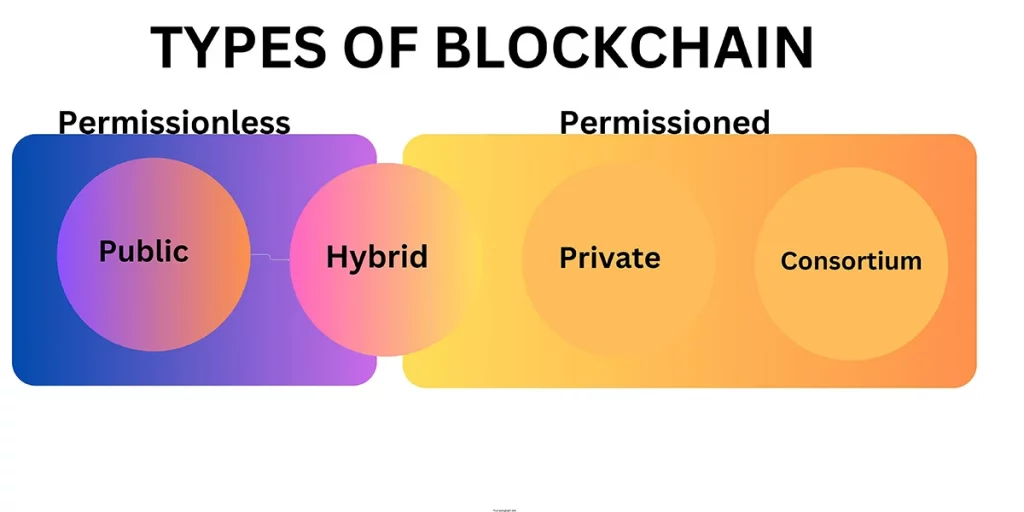
A public blockchain is a permissionless blockchain, and Private and consortium are permissioned blockchains. A hybrid blockchain is a combination of a permissioned and permissionless blockchain. A thorough knowledge of blockchains and types of blockchains will help to understand the application of blockchain and distributed ledger technology.
Application of blockchain technology
Cryptocurrency is one of the best examples of blockchain network consensus. Since the data is unalterable, there is no role for a middleman, third-party authenticator, or auditor. Bitcoin was introduced in 2008 by Satoshi Nakamoto during the Global Financial Crisis as the first practical application of blockchain technology. Cryptography secures messages from leaking to a third party through encryption and decryption.
Do you know why blockchains are attractive? It is a peer-to-peer network system without intermediaries. The information is stored chronologically in the chained system, similar to a ledger. Without intermediaries, it is least time-consuming, financially beneficial, and safe.
Blockchain in different sectors:
Blockchain is efficiently used in various sectors. A few of them are listed below:
Banking: It aids the customers to borrow money at low interest securely.
Health care: Helps to save and transfer patient data to hospitals and related mechanisms.
Government: It reduces cost and improves efficiency by readily availing the data.
Supply chain: Enables quick and cost-effective delivery of products and services.
Real estate: Investors pool the sum and purchase the asset as a shareholding.
Charities: Blockchain guarantees the donated amount to reach the legitimate beneficiaries.
Education: It securely stores and shares the academic record and is tamperproof.
Insurance: It provides better data and enhances transparent data sharing.
Automobiles: It is used in authenticating automobile parts, marketing, economic interactions, and vehicle tracking systems.
Energy: It is efficient in energy management, especially renewable energy.
Entertainment: It is helpful in distribution and licensing or royalty-related issues. It is also beneficial for the artists and co-production team to keep a verified account of their work.
Retail business: The retailers can access the details of a product’s origin and current position in case of fraudulent loss.
Legal services: In the e-court system, every case and document is digitalised in Indian courts. So, the lawyers and judges can digitally sign and save the documents for convenience and access.
Human resources: HR professionals can save the immutable documentation of each individual by limiting access to authorised persons. It eliminates the possibility of data breaches.
Agriculture: The backbone of the Indian economy is agriculture. Blockchain helps track information about plants, seeds, fertilisers, and climate-oriented farming techniques.
Potential challenges of blockchain technology
The blockchain network has three challenges: common, technical and organisational. The common or general challenge of blockchain networks is the scamming that happened in the initial period. Secondly, the private key should be secure and impossible to hack. But, if the auto-generated private key is lost, the account is unusable, which is one of the concerns of its users.
The technical challenges of blockchains include scalability and interoperability. The organisational challenges, like lack of awareness, regulation, return on investment, privacy, and security issues, can be eliminated by exploring the opportunities in blockchain technology.
Similarities of Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology
DLT and blockchain are immutable, decentralised, and time-stamped. To a certain extent, it is unshakable. Blockchain and distributed ledger technology can be public, private, or hybrid (a combination of public and permissioned) network systems. Both technologies use geographically distributed ledgers called nodes. In digital technology, the password or user ID is recoverable. But in blockchains, without a private key, the account is dead. There is no single-point failure of data in both technologies.
Identifying the difference
Now, let’s consider the differences between blockchain and distributed ledger technology. Not every DLT needs to use blockchain technology. So, Distributed Ledger Technology is partially dependent on blockchain. However, blockchain technology is one of the types of distributed ledger technology with an immutable digital signature. They are rather an advanced version of DLT.
Blockchains use encryption, and the blocks are added to the chain. They are transparent, and data is grouped, forming a blockchain, a unique feature of blockchain. Only certain forms of DLT use encryption. The transparency level or opaque level varies in DLT. The distributed ledger system need not depend on the block structure.
Conclusion
Blockchain is an immutable, tamperproof, peer-to-peer, shared, and decentralised ledger system that uses ‘Distributed Ledger Technology’. We are moving from traditional paper-based ledgers to modern digital ones. E-governance, e-courts, e-learning, and e-treasury reflect the shift of systems from the conventional to the digital era. In blockchain networks, blocks are signed digitally and are cryptographically hashed.
Distributed Ledger Technology and Blockchain Technology are even more advanced, with automatically triggering self-executable contracts, known as smart contracts. It is high time to consider sustainable growth by maintaining ecological balance. In this perspective, blockchain technology minimises resource usage. Except for the concern regarding private key mismanagement or loss, blockchains are user-friendly as well. In this digitally advanced twenty-first century, blockchain technology is a game changer.

