Imagine an internet kind that not only interprets what you input, but also accurately understands what you convey, no matter whether through text, voice or other media. Yes….it’s true. We’re living in an era where the content we consume is more tailored than ever before. We’re at the tipping point of a new phase in the web’s evolution which calls itself “Web 3.0”.
Paging back, Web 2.0 already realized many innovations energizing the user participation. It established a community web that interacted. There was tons of information load and real-time communications happening everywhere. The picture would have been perfect if it never threatened one’s privacy.
Hold on….privacy??? How?
To explain the crack, let’s take our Google/Facebook/LinkedIn account. Using these accounts, one can easily sign-in to multiple applications…right??
But…this “compatibility” feature has its own inherent threats also.
Do you know how??
Well… “agreeing” to the terms & conditions, one is actually giving these servers a consent to track your activities and access your personal information, say your online accounts, passwords, emails, drive content and much more. This definitely can raise a concern over one’s data privacy & security.
If you have your write ups or videos in any social media, do you think you really own the content? The social media companies have the right to withdraw your posts, delete your account and so on. Thus a third party like Facebook, Twitter, YouTube has the true authority over what you consider to be of “your own”.
In the early article we saw an example of how the failure of a centralized system could bring into stop the activities of millions. This article indeed proposes a solution to that mishap.
Here, we’ll see yet another dimension of web 3.0 which is “decentralization”.
The Decentralized Web
Web 3.0 introduced the concept of replacing the centralized systems with the decentralized systems. There is no single authority which controls Web 3.0. Rather it works on a peer-to- peer network that connects a group of devices called nodes (peers), where every peer acts both client and server.
Web 3.0 in large enables an open, trustless and permissionless networks. It will be built from an open source software that can be audited by the public. More on, the network participants can communicate with each other with no trusted third party influence. It simply allows anyone to join the network with no mess of governing bodies (permissionless).
Instead of storing data in centralized servers, in Web 3.0 applications, it will be stored in a distributed ledger. Blockchain and associated applications play an important role here in implementing the concept of decentralized web.
Let us see how.
Role of Blockchain in Web 3.0
Blockchain records the transactions between the users in its distributed ledger. Transactions are grouped into blocks and each block is cryptographically linked to its previous block. Every peer in the blockchain network, holds a copy of the ledger.
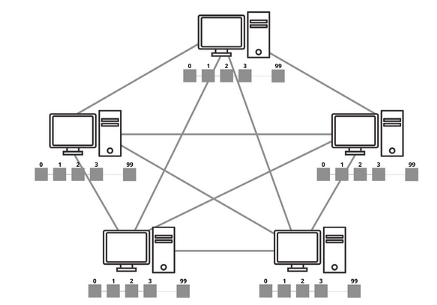
Here transactions are transparent. Strong cryptographic algorithms are used to ensure privacy of users. Users have full control over their data. All you need to access the network is a wallet. These are available as browser extensions, apps, and even hardware. A user’s wallet holds a public wallet address that is used to receive transactions and a private key that is used to sign and send transactions. User authentication is done through the user’s wallet.
A note on Web 3.0 will not be complete without a mention about tokens — a digital representation (code) of a value or asset that can be traded or transferred within a blockchain network. Cryptocurrencies like bitcoin and ether are the native tokens of a blockchain network which are often treated as an alternative to fiat currency. Smart contracts (programs running in blockchains) can create cryptographic tokens to represent any asset with few lines of code. Any item of value can be represented by tokens- license, passports, certificates, creative works, ownership of assets and so on. Value of a token will be the value of asset it represents. Tokens are secured by cryptographic techniques and can be exchanged without any intermediary.
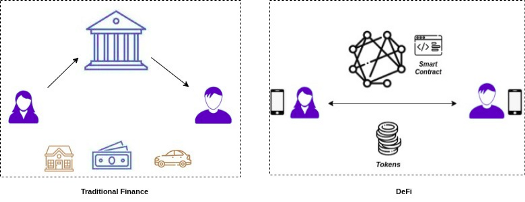
The “tokenization” concept gave rise to the concept of DeFi (Decentralized Finance). You may check this link for an introduction to DeFi.
Decentralization also helps to increase the reliability of the network. Unlike Web 2.0 servers, Web 3.0 servers never go down. There is no single point of failure. Even if some of the peers are faulty or act malicious, you still have the data within other peers.
How does blockchain manage to work without a central authority ?
Users decide the system and control the system. Usually organizations have top-down structures managed by contracts between various individuals. But Web 3.0 establishes a digital democracy controlled by a decentralized autonomous group of stake holders without any legal agreements between them. The rules are predefined and executed as computer programs running within the blockchain, called smart contracts. These smart contracts decide to allow or disallow the content and activities within the network. Since they are computer programs, the rules are automatically enforced. They are open source and hence available for public audit.
The network participants do not know each other. In other word, blockchain creates a “trustless” environment. The technique used to enforce network security is to incentivize the network participants. Peers who are providing service to the network, for example miners who verify and create the blocks, are given tokens as incentive.
Challenges of decentralization
Decentralized systems have some limitations compared to centralized systems. The transaction processing is slow and also costly. Implementation of Web 3.0 concepts is complex. The absence of a central authority makes peer co-ordination and conflict resolution a tedious task.
Elimination of third parties has certain risks also. For instance, it gives permission for everyone to publish any content on the web since there are no central body to censor it. A collaboration between government and tech enthusiasts is required to decide on the restrictions and policies to be implemented without adversely affecting the features of blockchain.
Though many applications based on Web 3.0 are available, it still remains as an abstract concept. Many areas and potentials of Web 3.0 are yet to be explored.
References: Ethereum.org
Image courtesy: Pinterest
